Embryonic Development Process: Key Stages & Growth Factors

Dr. Pujil Gulati, IVF Specialist with over 13 years of experience in Assisted Reproductive Techniques BabyBloom IVF Gurgaon
Embryonic development is a complex and fascinating process that transforms a single fertilized egg into a fully formed organism. This journey involves several key stages, each guided by genetic instructions and influenced by essential growth factors.
In this article, we will explore:
- ✅ Stages of Embryonic Development
- ✅ Key Growth Factors in Embryo Formation
- ✅ Importance of Each Developmental Stage
- ✅ Factors Affecting Embryo Growth
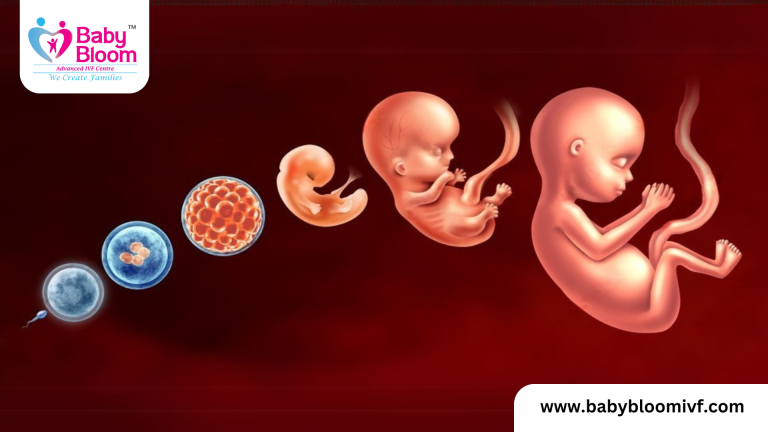
Stages of Embryonic Development
Embryonic development occurs in a step-by-step manner, beginning at fertilization and continuing until birth. The process is divided into five key stages:
1️⃣ Fertilization (Day 0)
- The process begins when a sperm cell fuses with an egg (oocyte) in the fallopian tube.
- This forms a zygote, a single cell containing genetic material from both parents.
- The zygote starts dividing through mitosis to create multiple cells.
2️⃣ Cleavage (Day 1-4)
- The zygote undergoes rapid cell division without increasing in size.
- It forms a morula, a solid ball of cells.
- Cells continue dividing until they form a blastocyst, a hollow structure ready for implantation.
3️⃣ Implantation (Day 5-9)
- The blastocyst travels to the uterus and attaches to the uterine lining (endometrium).
- The outer layer of the blastocyst develops into the placenta, which supports the growing embryo.
- The inner cells form the embryonic disc, which will develop into the baby.
4️⃣ Gastrulation (Week 2-3)
- The embryo forms three distinct layers:
🔹 Ectoderm – Becomes the nervous system, skin, and hair.
🔹 Mesoderm – Forms muscles, bones, and the circulatory system.
🔹 Endoderm – Develops into the digestive system, liver, and lungs. - These layers give rise to all major organs.
5️⃣ Organogenesis (Week 3-8)
- Major organs begin forming, including the heart, brain, and limbs.
- The neural tube closes, becoming the spinal cord and brain.
- The heart starts beating around Week 4.
- By Week 8, the embryo transitions into a fetus with fully developed basic structures.
Key Growth Factors in Embryo Formation
Growth factors are proteins that regulate cell division, differentiation, and tissue development. The most important growth factors in embryonic development include:
Fibroblast Growth Factors (FGFs)
- Control cell division and blood vessel formation.
- Essential for limb and organ development.
Bone Morphogenetic Proteins (BMPs)
- Help in bone and cartilage formation.
- Play a role in heart and kidney development.
Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) Protein
- Directs limb formation and brain development.
- Helps in proper positioning of organs.
Wnt Signaling Pathway
- Regulates cell movement and tissue formation.
- Essential for neural tube closure and spinal cord growth.
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)
- Promotes blood vessel formation.
- Ensures proper oxygen supply to the embryo.
Importance of Each Developmental Stage
- 📌 Fertilization – Determines genetic traits and kickstarts embryonic development.
- 📌 Cleavage – Rapid cell division prepares the embryo for implantation.
- 📌 Implantation – The embryo attaches to the uterus and starts receiving nutrients.
- 📌 Gastrulation – Forms the three germ layers that shape body structures.
- 📌 Organogenesis – Major organs and systems start functioning.
Each stage is critical, and any disruption can lead to developmental defects or pregnancy loss.
Factors Affecting Embryo Growth
Several factors influence the healthy development of an embryo:
Genetic Factors
- Chromosomal abnormalities can lead to miscarriage or birth defects.
- Genetic mutations may cause disorders like Down syndrome.
Maternal Health
- Poor nutrition, stress, and chronic diseases can affect embryo growth.
- Smoking, alcohol, and drug use increase the risk of birth defects.
Environmental Factors
- Exposure to radiation, toxins, or infections (e.g., rubella, Zika virus) can harm the embryo.
Hormonal Balance
- Proper levels of progesterone and HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) are needed for successful implantation and pregnancy maintenance.
Final Words
Embryonic development is a complex and highly regulated process, ensuring the formation of a healthy baby. From fertilization to organ formation, each stage plays a vital role in shaping life. Understanding key growth factors and external influences can help improve pregnancy outcomes and fetal health.
If you’re planning a pregnancy or undergoing fertility treatment, staying informed about embryonic development can be beneficial. 🍼💖
🔍 Stay healthy, stay informed, and nurture new life with care! 🚼 Book Your Free Consultation Today! Take the first step toward parenthood with a free IVF consultation. At BabyBloom IVF Centre
Write your message:-

Social Media Links :-
Welcome to BabyBloom IVF, where your journey to parenthood is nurtured with care, expertise, and the latest advancements in fertility treatment. Located in the heart of Gurgaon, Babybloom IVF is the Best IVF Centre in Gurgaon & leading fertility center dedicated to helping couples achieve their dreams of starting or growing their families.
Contact Us
Address No.1 I, block, 189, near Baani Square, South City II, Sector 50, (Gurgaon) Gurugram, Haryana 122018
Address No.2 Babybloom IVF, Nursing Home, Civil Rd, Company Bagh, Rohtak, Haryana 124001

Brought Happiness to the world
@BabyBloom IVF All Rights Reserved @2025


